
Bounced Email: Definition, Types & How to Prevent [2026]
So, you poured hours into crafting the perfect email campaign. You selected the most engaging visuals, wrote compelling email copy, and designed irresistible calls to action, all tailored to your audience’s needs. Then, you hit send, eagerly anticipating some great open and conversion rates.
However, your excitement quickly faded when you realized that your carefully crafted message didn’t reach your recipients’ inboxes.
But why? The answer is simple: your emails bounced back.
In this post, we’ll see the definition and the reasons behind bounced emails and show you how to minimize your bounce rates. By enhancing your email deliverability, you’ll ensure your future campaigns land precisely where they’re meant to—in the inboxes of your potential customers.

The easiest and most affordable email marketing and newsletter software!
What is a Bounced Email?
An email message that doesn’t reach the recipient’s inbox is considered an email bounce. This occurs when the email server provider (ESP) detects an email delivery error or failure and returns the message to the sender.
Common email bounce reasons include a non-existent email address, a full mailbox, and issues with the recipient’s email server.
Soft Bounce Vs. Hard Bounce
There are two types of email bounce, soft and hard.
A soft one is like a temporary hiccup in the email delivery process. The soft bounce code in your non-delivery report (NDR) will begin with ‘4’ and have three digits, and typically occur due to a recipient’s full inbox or spam and reputation issues.
On the other hand, when a message hard-bounces, you’ll see a three-digit code starting with ‘5’. You can check the code in the following hard bounce example from Gmail:
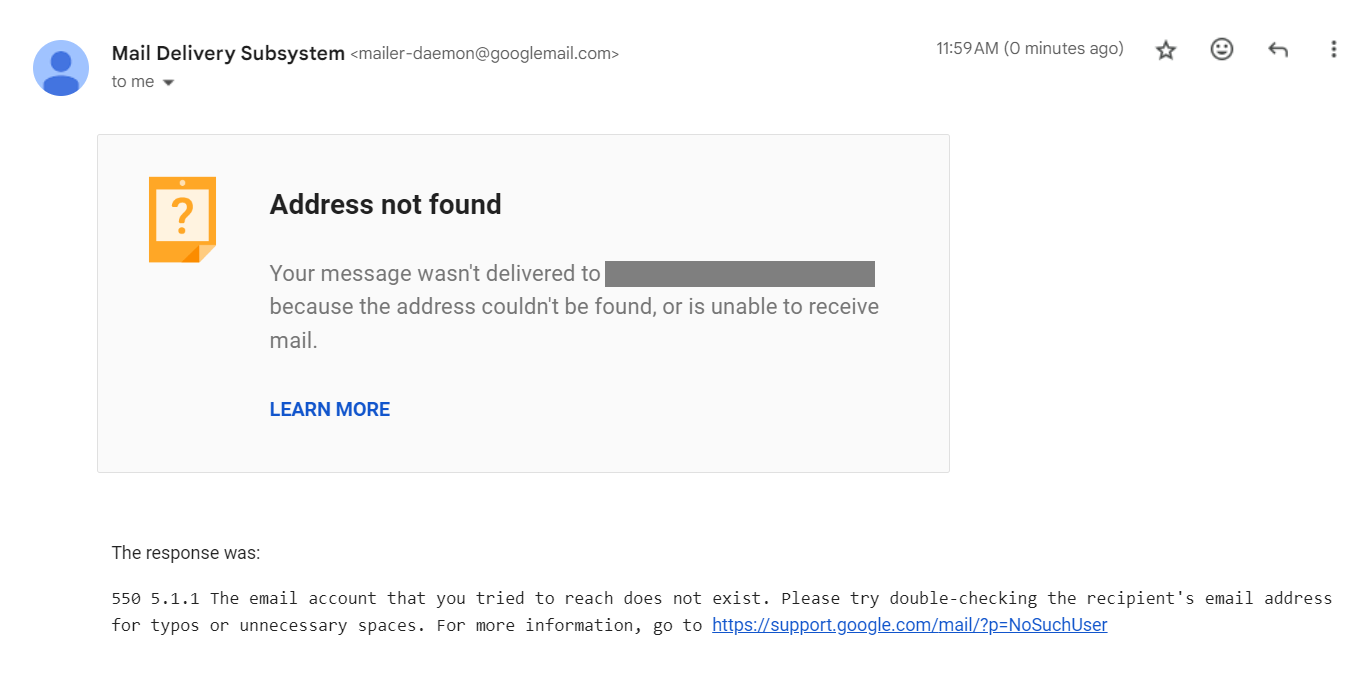
Non-existing domain names and invalid email addresses (due to typos) are usually some of the reasons for hard bounces.
Moreover, your bounce rates greatly affect your email deliverability, so keeping them low, especially with hard bounces, is crucial for maintaining a strong email reputation.
Blocked vs. bounced emails
While people usually tend to distinguish between blocked and bounced emails, blocked emails are, in fact, a type of bounce that affects your deliverability in the same way.
Here’s why a block might happen:
- Your reply-to address is on a block list.
- One of the IP addresses used by your ESP is temporarily blocked.
- One of your domains is temporarily blacklisted.
- The receiving server only accepts emails from pre-approved senders (Outlook).
Whether your email has bounced back, or been blocked, it harms your sender reputation and can negatively impact your ability to successfully deliver future emails.
While it may seem like a serious and permanent issue, there are certain things you can do to get unlisted, such as contacting the blocklist operator and cleaning your email list.
For more information, check our dedicated email blacklist post on what to do and how to avoid it.
Common Reasons Why Emails Bounce Back
As mentioned, email bounce can hurt email deliverability, leading servers to see your messages as spam and possibly blocking them automatically.
Emails may bounce for a variety of reasons. We saw some of these reasons above. Here is the full list to keep in mind:
- Invalid recipient email address (due to typos).
- Recipient’s mailbox is full.
- User is on vacation or out of office and has set auto-replies.
- Issues with the recipient’s email server, such as outages.
- Email message size exceeds the server limits.
- The recipient’s mail server is temporarily unavailable.
- Email flagged as spam by user’s server or spam filters.
- The sender’s domain or IP address is blacklisted.
- Authentication failure due to DMARC, SPF or DKIM misconfiguration.
- Email accounts no longer exist or have been suspended.
Now that you know why your campaigns may bounce back, let’s see how to find your bounce rate.
How to Calculate Your Email Bounce Rate
The bounce rate is among the most important email marketing metrics. It stands for the percentage of undelivered emails to your subscribers.
You can calculate it by dividing the number of hard bounces by the number of emails sent, and then multiplying that number by 100.
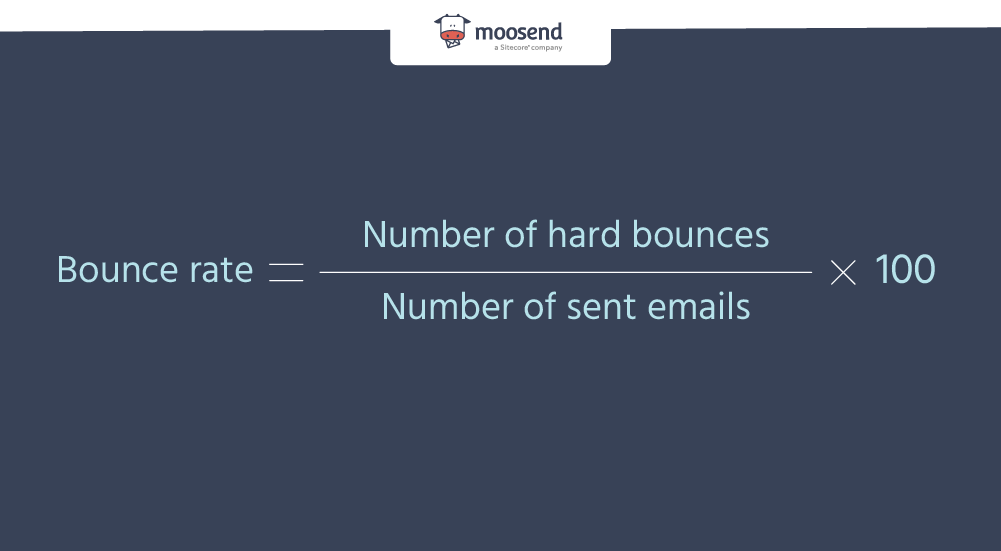
Having some bounces is unavoidable. However, as an email marketer, you want to monitor your rate because it’ll inform you how effective your email campaigns are.
A reliable ESP (Email Service Provider) will provide you with detailed bounce and other email tracking reports. Moosend, for example, will offer bounce reason insights to help you identify the issue:
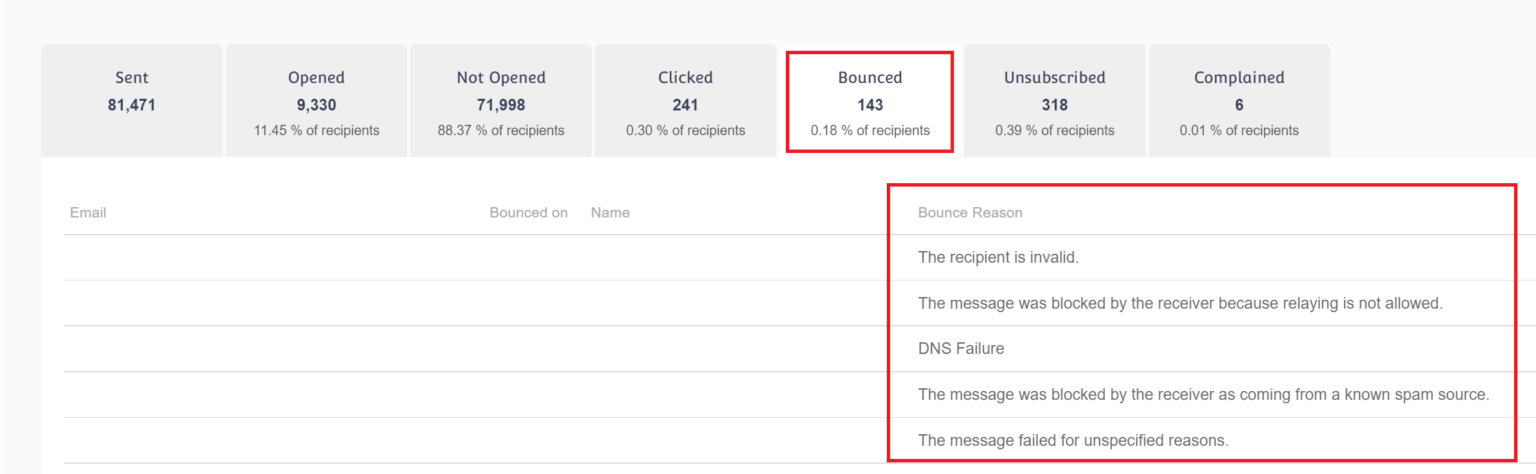
If you want to have complete control over your performance, consider registering for a Moosend account. With detailed reporting and analytics, you can monitor your metrics and optimize them accordingly.
What is a good email bounce rate?
A bounce rate higher than your industry benchmark could signal issues with your email list quality or segmentation.
On the other hand, a high bounce rate could mean your emails don’t resonate with your audience or aren’t properly optimized for deliverability.
Ideally, your email bounce rates should be below 2%, which generally counts as a good benchmark.
Bear in mind that email service providers might penalize your sender reputation if your bounce rate exceeds 5%. This would have a significant negative effect on your email marketing campaigns.
Even if your email bounce rate is below average, systematically addressing various factors that influence them is important to maintain your good sender reputation and email deliverability.
How to Prevent Emails from Bouncing
You can use various approaches to influence the factors that contribute to higher bounce rates.

1. Keep your email list clean
Regularly clean your email list by removing invalid email addresses and outdated or inactive ones.
Having technical limitations and time constraints in mind, it may not be practical to remove email addresses manually. A fitting verification tool might be a better option.
Also, consider initiating a campaign targeting disengaged contacts, asking if they still wish to receive your emails.
These actions will help you improve your sender reputation and reduce the risk of bounces, all while requiring minimal time investment.
2. Verify email addresses
Implement a double opt-in process to verify email addresses during signup. It means your potential subscriber will get an authentication email and only be added to your list after clicking the confirmation button.
Here’s an example by Instacart:
This ensures that you have accurate contact information and reduces the likelihood of bounces.
3. Craft engaging content
More than half of all emails sent worldwide are considered spam. Even though your emails are most likely not, creating compelling and relevant content, from subject lines to CTAs, will ensure they don’t get classified as such.
Email segmentation is also a great way to send personalized content tailored to your subscribers’ needs and expectations.
4. Avoid “spammy” words
Certain words may contribute to your emails being labeled as spammers. Try to avoid them as much as possible. Here are some of them:
- FREE CASH
- Loans
- Free job opportunity
- Sharp
- Violence-related words
For a more detailed list of spam-related words, check out our in-depth guide.
Also, if you have trouble creating subject lines, you could use a subject line tester like Refine to help you write and optimize them.
Moosend’s AI-powered tools include a built-in AI subject line generator and AI writer to streamline your process.
5. Manage Email Frequency
If you don’t email your subscribers regularly, they might not recognize you, and your emails could get spam complaints.
But if you send too many emails, they might experience subscriber fatigue.
It’s best to set expectations for how often you’ll email your subscribers and stick to a consistent schedule.
Lower Your Email Bounce Rates
You can now stop wasting resources on sending emails that might ultimately bounce.
But, before you go off to calculate your email bounce rates, clean your email list and up your email content game—one last thing: Your ESP choice greatly influences bounce rates.
A reliable platform will provide you with detailed bounce reports and prevent spam issues, which are crucial for successful campaigns.
At Moosend, hard-bounced email addresses go to a suppression list, preventing them from receiving future campaigns and safeguarding your sender’s reputation.
You can take control of your email metrics by register for a free email account and experience its capabilities firsthand.
FAQs
Here are some simple answers to common questions about email bounce.
1. What is an email soft bounce?
An email soft bounce occurs when the recipient’s email server temporarily rejects the email, often due to a full inbox or server issues.
2. What is an email hard bounce?
An email hard bounce happens when the email is permanently rejected by the recipient’s server, typically due to an invalid email address or domain name.
3. How will you know if your email bounced?
You will get a non-delivery report from your email server—an email informing you of delivery failure and the reason your email was rejected. NDRs will provide clues about what might be wrong with your email deliverability, enabling you to fix any issues.
4. How do you handle an email bounce?
You can start by reviewing the bounce message for details, updating the recipient’s contact information if necessary, and retrying delivery. For hard bounces, consider removing the email address from your list as it may not exist.
5. Should I delete bounced emails?
No, you shouldn’t delete them. Instead, use suppression lists to protect your sender reputation and update your CRM to avoid problems. Identify patterns and monitor bounces to take prompt action and maintain a clean list for optimal deliverability.
6. What is email reputation?
It refers to the perception of an email sender’s trustworthiness and reliability by email service providers (Gmail, Yahoo, etc.). It’s determined by factors such as your sender score, email engagement, spam complaints, and adherence to email marketing best practices.


 Published by
Published by
 Published by
Published by