
Customer Survey Best Practices to Protect Respondent Data [2026]
Customer surveys are a goldmine of data. They tell you exactly what your customers want, patterns that influence their buying decisions, and how to retain their loyalty.
But here’s the problem: you’re not the only one eyeing that data.
As many customer surveys contain personal and behavioral information, cybercriminals are eager to obtain them. In the first quarter of 2025 alone, the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) has reported 824 major data breach incidents.
For affected customers, this means exposure to identity theft, financial fraud, phishing attacks, and long-term damage to their credit scores. Failing to protect your customers doesn’t just expose them to dangers; it can also become a PR and legal nightmare for your organization.
In this guide, we’ll explore the types of data businesses collect through surveys, how it’s typically gathered, and essential customer survey best practices to follow for maintaining its security.
What Type of Data Do Customer Surveys Collect?
Customer surveys are designed to help businesses better understand their audience, which means they often collect a wide range of data. The exact type of information gathered depends on the company’s goals and the survey’s purpose.
Personally identifiable information (PII)
Any information that can identify an individual, on its own or when combined with other data, is considered Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
This includes a customer’s full name, phone number, home address, email address, or date of birth.
PII is a prime target for cybercriminals. It can be used for identity theft or sold on the dark web for profit.
Demographic information
This includes age, gender, income bracket, occupation, and education level.
While this data helps businesses build customer segments and tailor their marketing efforts, it also provides hackers with enough context to craft convincing phishing or social engineering attacks.
Behavioral insights
Understanding how customers interact with your product, what they enjoy, what they avoid, and how often they engage helps shape better product experiences.
However, this behavioral data can also be exploited by malicious actors (such as impersonators and scammers) to mimic user behavior or manipulate customers more effectively.
Transactional data
Surveys may include questions about past purchases, preferred payment methods, or general spending habits. While useful for understanding buying behavior, this financial data can give cybercriminals deeper insight into a customer’s routines, making their scams more convincing and more complex to detect.
Location and device data
Many surveys also collect metadata such as IP addresses and device types. On their own, these details might seem harmless. But when combined with other information, they can help hackers map a user’s digital footprint and launch more targeted social engineering attacks.
How Businesses Collect Survey Data
Thanks to advancements in technology, launching surveys and collecting data has become easier than ever.
Companies now have so many ways to connect with customers and collect their feedback.
Online survey tools
Google Forms, Typeform, SurveyMonkey, and other dedicated survey tools allow businesses to collect survey data in an organized and scalable way.
Some of these tools also support integrations with customer relationship management (CRM) systems, email automation tools, and data analytics platforms.
Onsite forms
Some companies might choose to host surveys on their website using on-site forms instead of relying on dedicated survey platforms.
This gives them more control over the design and structure of the survey. However, it might not be as scalable as a dedicated survey platform.
Email surveys
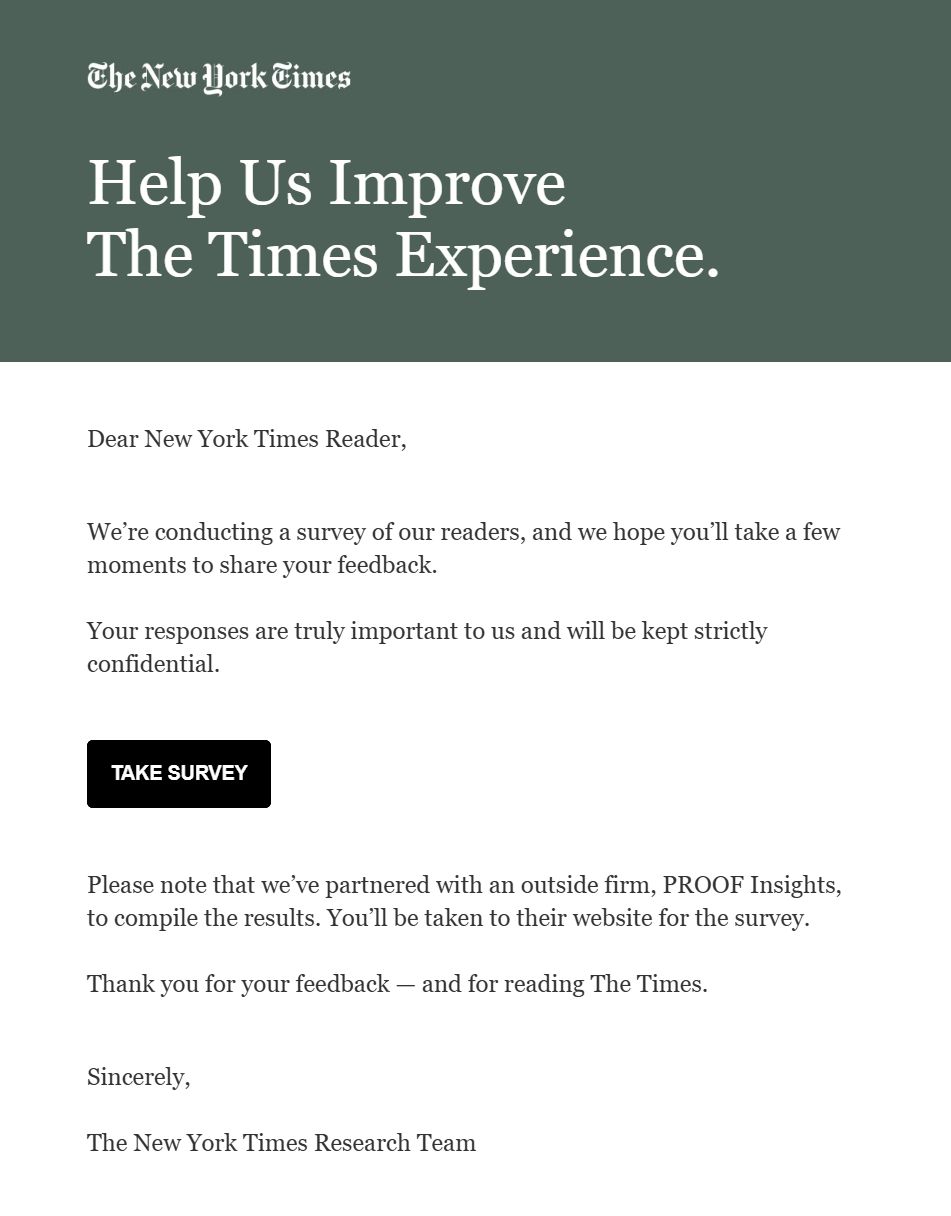
Email ranks among the best ways to reach customers with surveys. Companies often include links to their surveys or simply embed the questions within the email body. Email surveys typically have high engagement rates because they’re designed for a warm audience, are easily accessible, and can be personalized.
Here’s an example from The New York Times:
Social media surveys
Social media platforms like X, Instagram, and Facebook offer built-in tools for running quick, informal surveys.
These are often part of broader engagement strategies, designed to feel natural within the platform’s environment.
For example, a clothing brand might use Instagram Stories to poll followers about their favorite summer looks, blending data collection with real-time interaction.
Customer Survey Best Practices for Protecting Respondent Data
As technology advances, hackers become increasingly sophisticated and creative, pushing the boundaries of existing security protocols.
According to Check Point, the first quarter of 2025 recorded an average of 1925 cyberattacks per week, a 48% rise compared to the same quarter in 2024.
So, if you’re serious about protecting your respondent data from these malicious groups, now is the time to step up your game.
1. Encrypt your respondent data
Encryption works by turning readable information (plaintext) into unreadable formats (ciphertexts). That way, even if an unauthorized person intercepts the information, they won’t be able to make sense of it.
Start by ensuring your surveys are shared using HTTPS. This keeps the survey data encrypted during transmission (after the respondent has submitted their data). Additionally, utilize encrypted databases to ensure the data remains secure during storage.
If you’re using a survey platform, carefully assess its security features and how it handles data encryption. The best platforms adhere to the latest encryption standards (such as AES-256 for stored data) and regularly update their approach to match prevailing security scenarios.
Hosting your own data gives you more control over how it’s secured and accessed. Just ensure you employ robust encryption mechanisms to prevent exposure.
2. Only collect what you need
While running customer surveys for your integrated marketing campaigns, you may be tempted to collect as much data as possible, including details that aren’t critical for your research.
First, major privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, are built around the principle of data minimization. That means collecting unnecessary data can be a violation, even if you don’t misuse it.
Second, the more data you collect, the greater the potential reward for hackers. In the event of a breach, limiting what’s exposed can significantly reduce the impact. Unnecessary data only increases the risk.
Before launching your survey, clearly define what information you actually need. If you include optional questions, make that clear and explain why you’re asking. It shows respect for your customers’ privacy and builds trust.
3. Anonymize responses
Always prioritize structuring your surveys in a way that doesn’t collect personally identifiable information, such as emails, full names, and location details.
In situations where you need such details for follow-ups or rewards, make sure you use tools that automatically separate the identifying information from the survey responses. Many affordable email marketing platforms offer built-in features to securely handle this kind of data separation.
When the survey responses and identifying information are separated, two datasets are generated. Anonymization works by using a unique identifier to link the two datasets without directly connecting them to the primary research data.
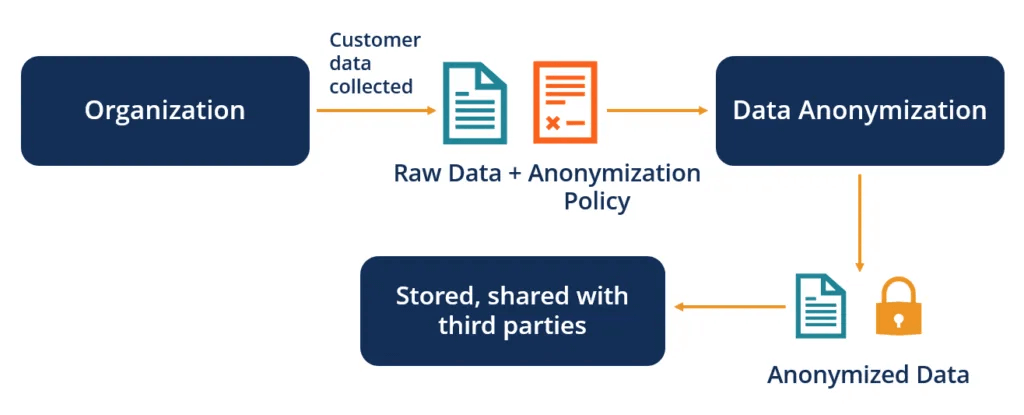
That way, when reviewing survey results, you’re not handling personal information, but making the core research data far less sensitive from a privacy perspective.
4. Don’t keep the survey data for longer than needed
Data privacy and security regulations require you to discard customer data once it has served its original purpose. The longer data remains in your system, the greater the opportunity it creates for potential breaches.
To prevent this, establish a strict data retention policy before launching your customer survey. Then, define how long the collected data will be stored in your repository for analysis, reporting, and follow-ups.
Also, to prevent oversight errors, automate the deletion of this data and schedule regular audits to ensure that you’re not retaining outdated data.
When deleting customer data, ensure that no traces remain by overwriting it multiple times. If you’re using online survey platforms, always inquire about their policies and features regarding data retention and deletion.
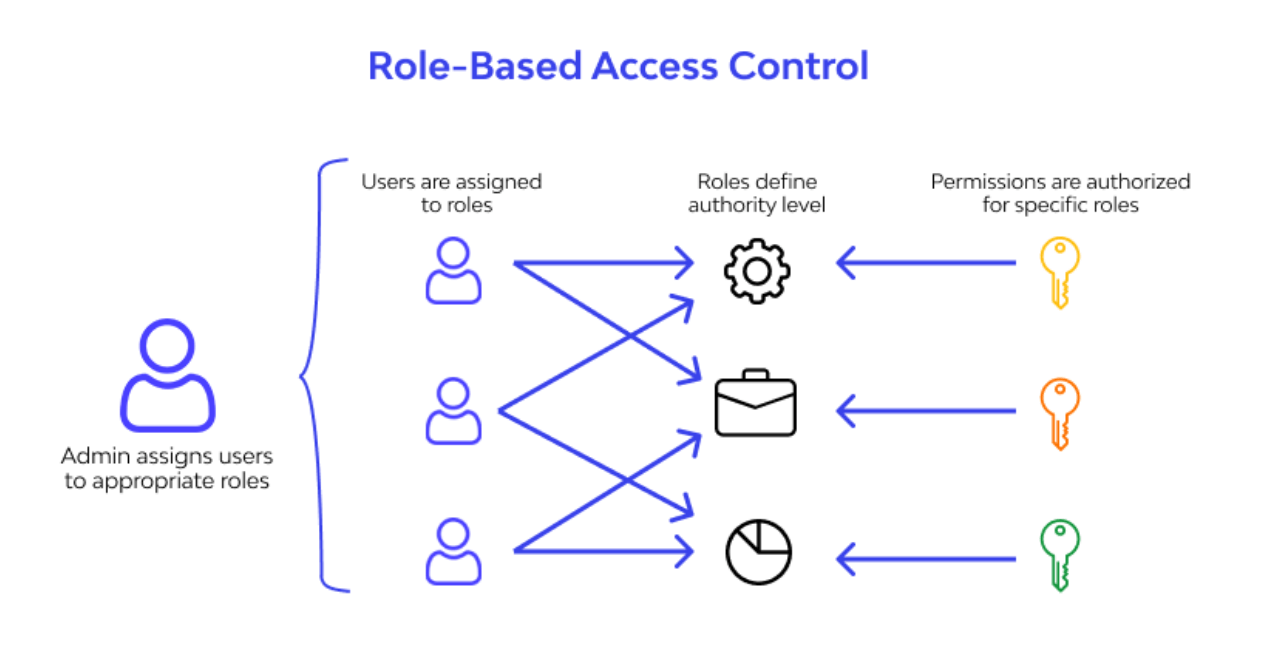
5. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) mechanisms
RBAC is a security approach that restricts system access based on a user’s role within the organization. It ensures that only authorized individuals can access specific data and only in ways that align with their responsibilities.
When setting up RBAC, define what data each role can access and what actions they can take. Follow the principle of least privilege, which means users should have only the minimum access necessary to perform their jobs and no more.
Where possible, mask sensitive data so users only see what they’re permitted to. This adds an extra layer of protection without disrupting workflows.
Then, use audit logs to track who gained access to the stored data, when it occurred, and what actions were taken with it. Regularly review these logs and set up alerts for suspicious behavior, such as repeated login failures or logins from unknown devices or locations.
This approach is particularly critical in environments such as call centers, where multiple agents and managers may require different levels of access to customer data. Proper access control not only strengthens security but also supports accurate analytics by ensuring only clean, authorized data is used for performance tracking.
6. Maintain a regular schedule for security audits
Data security is an ongoing process because hackers don’t take breaks. They constantly switch strategies and explore different angles to penetrate even the most secure systems.
If you must keep them at bay, never get too comfortable or assume your systems are impenetrable. Set a schedule for security audits to review your current security systems for vulnerabilities. This helps you spot loopholes early and stay ahead of cybercriminals.
Also, ensure you’re monitoring guidelines from relevant data privacy and security regulators, such as GDPR and CCPA. These bodies continually adjust their policies in response to current realities.
Always document each audit and track any issues discovered along with every improvement made.
7. Have a solid incident response plan
An incident response plan should be a big part of your security practices. This is because there’s always a chance of a security incident, regardless of how robust your security systems are.
Your incident response plan should clearly outline the actions that must be taken immediately after a breach occurs. Processes such as system isolation, incident investigation, and threat elimination, especially when managed through tools like AI-powered ticketing, should be well-documented with clear steps to accomplish them.
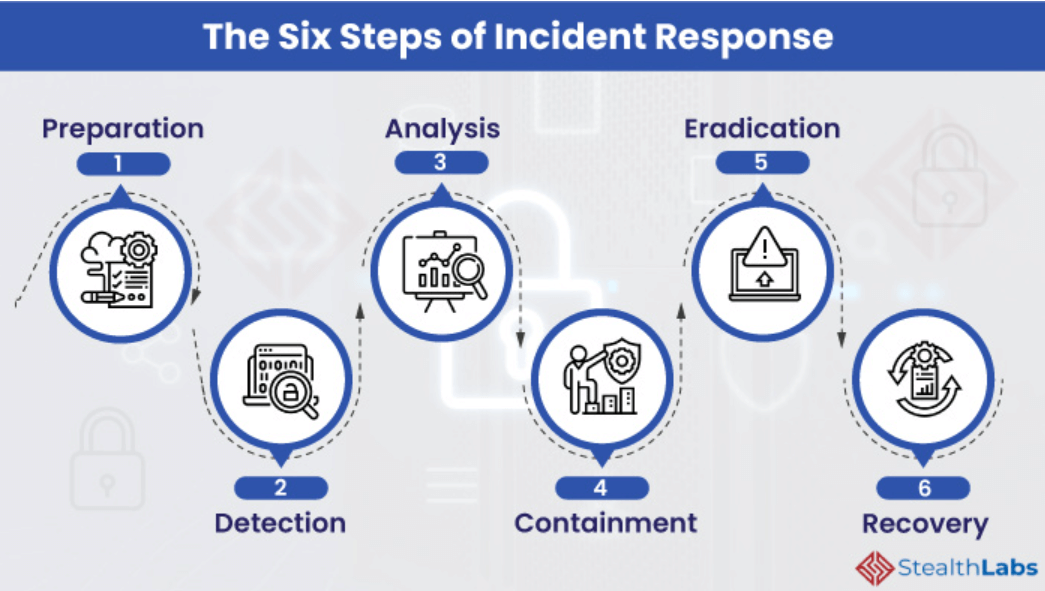
In your incident response plan, define roles beforehand:
- Who’s responsible for sending out notifications?
- Who’s responsible for containing the breach?
- Who’s accountable for documentation?
This keeps your team prepared ahead of time. So, if anything happens, you’re always prepared to take action.
8. Stay compliant with relevant data protection policies
Data protection policies, such as the GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, exist to help you stay on top of security threats.
Ignoring their guidelines will not only expose you and your customers to risks but also land you in trouble.
Depending on your industry and the jurisdiction in which your business is established, the data protection policies applicable to you can differ.
These policies are constantly changing in response to evolving security concerns. Always have their updated guidelines and review them against your current security systems. That way, you’ll never be caught off guard by cybercriminals or auditors.
9. Be more careful with your third-party integrations
While third-party integrations can improve workflows and system performance, they also introduce new vulnerabilities. Each connected app adds to your overall “attack surface,” giving cybercriminals more potential entry points.
That doesn’t mean you have to choose between efficiency and security. It just means you need to be selective and intentional about which tools have access to your survey data, and how much they can see or do.
According to SecurityScorecard, at least 35.5% of data breaches in 2024 originated from third-party compromises.
Before integrating any third-party application, carefully review their security documentation to ensure they adhere to the highest security standards. Prioritize platforms that hold strong certifications, such as SOC-2 and ISO 27001.
Also, ensure that you limit the amount of data each integration is permitted to access, focusing only on those that are necessary to prevent identity theft.
10. Educate your team
According to Infosecurity, 95% of data breaches happen as a result of human error. Without proper training and enlightenment, employees can pose the biggest threats to data security.
Here are some simple steps to follow:
- Host interactive sessions or webinars with your team to raise awareness about current security threats and hacker strategies.
- Educate employees on social engineering tactics, including how attackers manipulate people into sharing confidential information.
- Train them to recognize suspicious emails, especially those with urgent language or unexpected requests.
- Instruct them never to click on links or download attachments from unknown or unverified senders.
Most importantly, encourage them to keep learning. Cybercriminals are constantly changing their strategies, and employees need to stay on top of every new development. They must understand that cybersecurity isn’t an IT problem but a responsibility for everyone.
What to Do in Case of a Data Breach
Data breaches can happen to anyone, regardless of how robust their security protocols are.
So, if you ever fall victim, don’t beat yourself up or start pointing fingers. Every second counts, and you don’t want to waste it on a panic attack.
Contain the breach immediately
The first step is to find the source of the breach and isolate it immediately. If finding the compromised system is difficult, you may need to disconnect all devices that have access to your database. This includes analytics tools, CRMs, internal applications, etc.
It might feel drastic to disconnect so many systems, but in the immediate aftermath of a suspected breach, it’s much better to err on the side of caution. You need to secure the environment before you can properly investigate and remediate it.
Secure your backup data and double-check its integrity
Once you’ve contained the breach, check your backup systems to confirm that they’ve not been compromised as well.
If they’re still clean, make copies and store them separately. We strongly recommend encrypting your backups and storing them offline.
Gather forensic evidence
Before making any significant changes to the compromised systems, you must collect forensic evidence. Focus on items such as server logs, traffic data, system snapshots, database queries, and any other information that can reveal when and how the breach occurred.
Set up write blockers to prevent overwriting any critical evidence. If possible, create a full disk image of the affected systems. This will enable forensic investigators to determine how the breach occurred and the extent to which it penetrated.
Assess the scope of the breach
Perform a thorough analysis of the data breach to understand exactly what the hackers gained access to.
Identify all PII, financial data, health information, and other sensitive customer details that may have been exposed. Make a list of these and prioritize them according to the level of sensitivity and potential damage.
Verify whether the breach involves passwords, payment details, or other sensitive data points. This will help you understand the extent of the breach and also provide facts to those who require them.
Notify relevant authorities and affected customers
In many cases, you might need to report this incident to authorities within a specified timeframe, although it depends on your industry and jurisdiction. GDPR, for instance, requires a report to be submitted within 72 hours.
Prepare a detailed report describing the incident, the evidence you have, and what steps you’ve taken to contain the breach and bounce back.
More importantly, you need to inform your customers. Create a clear and concise message for them explaining the situation. Let them know that the company is working with the relevant authorities to control the situation and get to the root of the problem. Also, enlighten them on what they must do to protect themselves, like changing their passwords or monitoring credit reports.
Find the root cause and start corrective measures
Document the entire chain of attack, including the entry point, escalations, and actions taken by the attacker.
Ask yourself the following questions:
- What loopholes did the perpetrators exploit?
- Was there a vulnerability in your third-party integrations?
- Was your password policy not strong enough?
- Did an in-house staff fall for a phishing attack?
- Or was it something entirely different?
Based on the outcome of your root cause analysis, start implementing corrective procedures. This may involve updating software, decommissioning legacy systems, revising password policies, disconnecting specific applications, and implementing more stringent data protection strategies.
Your Customer’s Data Is Your Responsibility
When customers give you their data, they essentially give you a piece of themselves. By hitting the “submit” button, they’re trusting that you’ll go above and beyond to keep their data safe.
However, cybercriminals don’t care. They’re constantly on the prowl, looking for new ways to breach that trust.
Following the best practices discussed in this guide will help you keep hackers at bay, stay on the right side of the law, and seal your place as a trusted brand.



 Published by
Published by
 Published by
Published by

 Published by
Published by